MCP-Airflow-API
Model Context Protocol (MCP) server for Apache Airflow API integration. This project provides natural language MCP tools for essential Airflow cluster operations.
Note: To minimize operational risk, this MCP server currently focuses on read-only (query) operations only. APIs that modify the target Airflow cluster (e.g., triggering or pausing DAGs) are planned but currently on hold.
Tested and supported Airflow version: 2.10.2 (API Version: v1) and WSL(networkingMode = bridged)
Example Query - List DAGs
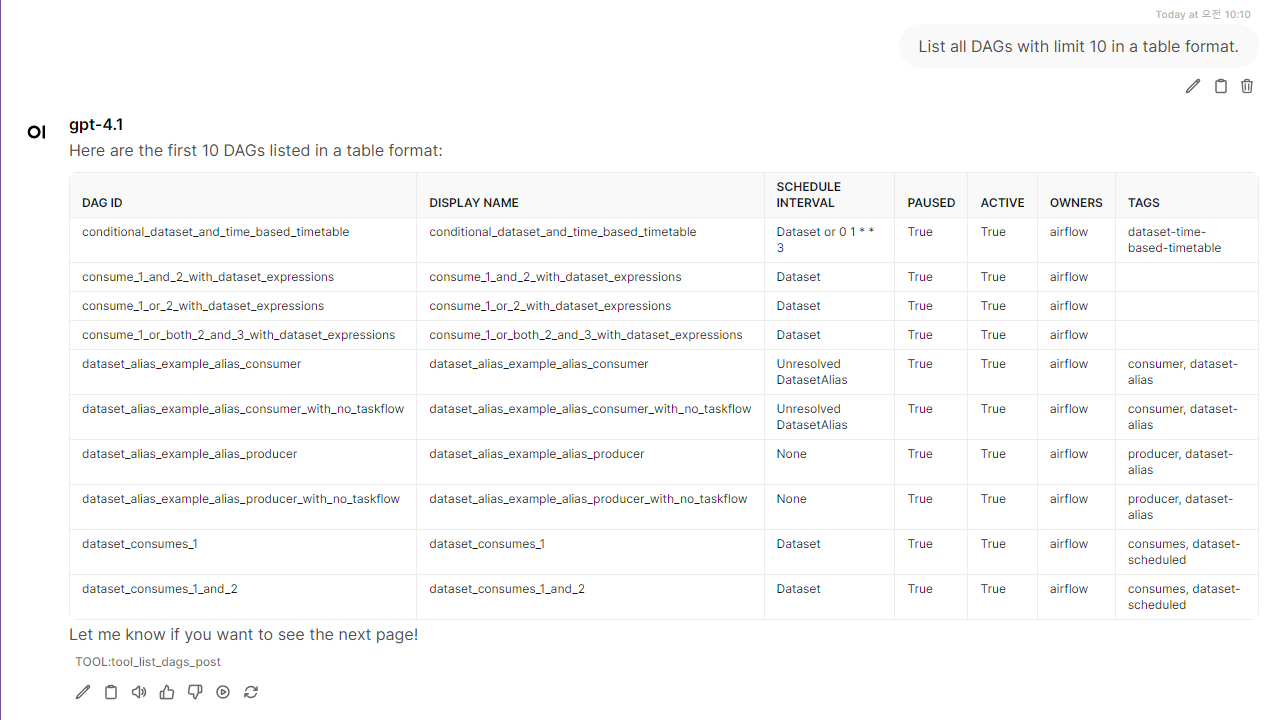
Usages
This MCP server supports two connection modes: stdio (traditional) and streamable-http (Docker-based). The transport mode is automatically determined by the MCP_SERVER_PORT environment variable.
Method 1: Local MCP (transport="stdio")
{
"mcpServers": {
"airflow-api": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["--python", "3.11", "mcp-airflow-api"],
"env": {
"AIRFLOW_API_URL": "http://localhost:8080/api/v1",
"AIRFLOW_API_USERNAME": "airflow",
"AIRFLOW_API_PASSWORD": "airflow",
"AIRFLOW_LOG_LEVEL": "INFO"
}
}
}
}
Method 2: Remote MCP (transport="streamable-http")
{
"mcpServers": {
"airflow-api": {
"type": "streamable-http",
"url": "http://host.docker.internal:18002/mcp"
}
}
}
Transport Selection Logic:
- stdio mode: When
MCP_SERVER_PORTenvironment variable is NOT set - streamable-http mode: When
MCP_SERVER_PORTenvironment variable is set
QuickStart (Demo - streamable-http): Running OpenWebUI and MCP-Airflow-API with Docker
- Prepare an Airflow Demo cluster
- Try this: Airflow-Docker-Compose
- (Optional) See Official Airflow Docker Install Guide
- Install Docker and Docker Compose
- Ensure Docker Engine and Docker Compose are installed and running
Setup and Configuration
- Clone and Configure
git clone <repository-url>
cd MCP-Airflow-API
- Ensure mcp-config.json
- Check and edit
mcp-config.json.http - The file is pre-configured for streamable-http transport
- Ensure docker-compose.yml
- Check Network Port numbers that you want.
- (NOTE) This Tested on WSL2(networkingMode = bridged)
- Start the Docker Services
docker-compose up -d
Service Access and Verification
- Check MCP Server REST-API (via MCPO Swagger)
- Access: http://localhost:8002/docs
- Verify all Airflow API endpoints are available
- Access Open WebUI
- URL: http://localhost:3002
- The interface includes integrated MCPO proxy support
- Register the MCP server
- In [Settings] — [Tools], add the API address of the “airflow-api” tool (the link displayed in the MCPO Swagger), e.g., http://localhost:8001/airflow-api
- Setup LLM
- In [Admin Pannel] - [Setting] - [Connection], configure API Key for OpenAI or Ollama.
- Completed!
Docker Configuration
The project includes a comprehensive Docker Compose setup with three separate services for optimal isolation and management:
Services Architecture
open-webui: Web interface (port 3002)
- Custom Open WebUI with integrated MCPO proxy support
- Built from
Dockerfile.OpenWebUI-MCPO-Proxy
mcp-server: MCP Airflow API server (port 18002, internal 18000)
- FastMCP-based MCP server with Airflow API tools
- Built from
Dockerfile.MCP-Server(Rocky Linux 9.3, Python 3.11) - Runs http transport when
MCP_SERVER_PORTis set
mcpo-proxy: MCP-to-OpenAPI proxy (port 8002)
- MCPO proxy for converting MCP tools to REST API endpoints
- Built from
Dockerfile.MCPO-Proxy(Rocky Linux 9.3, Python 3.11) - Provides Swagger documentation at
/docs
Configuration Files
The Docker setup uses these configuration files:
docker-compose.yml: Multi-service orchestrationmcp-config.json.stdio: MCPO proxy configuration for stdio transportmcp-config.json.http: MCPO proxy configuration for streamable-http transportDockerfile.MCPO-Proxy: MCPO proxy container with Rocky Linux 9.3 baseDockerfile.MCP-Server: MCP server container with FastMCP runtime
Environment Variables
The MCP server container uses these environment variables:
MCP_SERVER_PORT=18000: Enables streamable-http transport modeAIRFLOW_API_URL: Your Airflow API endpointAIRFLOW_API_USERNAME: Airflow usernameAIRFLOW_API_PASSWORD: Airflow password
Service Access
- Open WebUI: http://localhost:3002
- MCP Server: http://localhost:18002
- MCPO Proxy: http://localhost:8002
Container-to-Host Communication
The configuration uses host.docker.internal:18002 for proper Docker networking when connecting from containers to host services.
Features
- List all DAGs in the Airflow cluster
- Monitor running/failed DAG runs
- Trigger DAG runs on demand
- Check cluster health and version information
- Minimal, LLM-friendly output for all tools
- Easy integration with MCP Inspector, OpenWebUI, Smithery, etc.
- Enhanced for Large-Scale Environments: Improved default limits and pagination support for enterprise Airflow deployments (100+ to 1000+ DAGs)
Environment Variables Configuration
Required Environment Variables
These environment variables are essential for connecting to your Airflow instance:
AIRFLOW_API_URL: The base URL of your Airflow REST API endpoint- Example:
http://localhost:8080/api/v1 - Example:
https://airflow.company.com/api/v1
- Example:
AIRFLOW_API_USERNAME: Username for Airflow API authentication- Example:
airflow - Example:
admin
- Example:
AIRFLOW_API_PASSWORD: Password for Airflow API authentication- Example:
airflow - Example:
your-secure-password
- Example:
Transport Control Variables
MCP_SERVER_PORT: Controls the transport mode selection- When NOT set: Uses stdio transport (traditional MCP mode)
- When set: Uses http transport (Docker mode)
- Example:
18000(for Docker container internal port)
Optional Configuration Variables
AIRFLOW_LOG_LEVEL: Controls logging verbosity- Values:
DEBUG,INFO,WARNING,ERROR - Default:
INFO
- Values:
Available MCP Tools
DAG Management
list_dags(limit=20, offset=0, fetch_all=False, id_contains=None, name_contains=None)Returns all DAGs registered in the Airflow cluster with pagination support. Output:dag_id,dag_display_name,is_active,is_paused,owners,tags, plus pagination info (total_entries,limit,offset,has_more_pages,next_offset,pagination_info)Pagination Examples:
First 20 DAGs:
list_dags()Next 20 DAGs:
list_dags(limit=20, offset=20)Large batch:
list_dags(limit=100, offset=0)All DAGs at once:
list_dags(limit=1000)id_contains="etl"→ Only DAGs whosedag_idcontains "etl"name_contains="daily"→ Only DAGs whosedisplay_namecontains "daily"If both are specified, only DAGs matching both conditions are returned
running_dagsReturns all currently running DAG runs. Output:dag_id,run_id,state,execution_date,start_date,end_datefailed_dagsReturns all recently failed DAG runs. Output:dag_id,run_id,state,execution_date,start_date,end_datetrigger_dag(dag_id)Immediately triggers the specified DAG. Output:dag_id,run_id,state,execution_date,start_date,end_datepause_dag(dag_id)Pauses the specified DAG (prevents scheduling new runs). Output:dag_id,is_pausedunpause_dag(dag_id)Unpauses the specified DAG (allows scheduling new runs). Output:dag_id,is_paused
Cluster Management & Health
get_healthGet the health status of the Airflow webserver instance. Output:metadatabase,scheduler, overall healthstatusget_versionGet version information of the Airflow instance. Output:version,git_version,build_date,api_version
Pool Management
list_pools(limit=20, offset=0)List all pools in the Airflow instance with pagination support. Output:pools,total_entries,limit,offset, pool details with slots usageget_pool(pool_name)Get detailed information about a specific pool. Output:name,slots,occupied_slots,running_slots,queued_slots,open_slots,description,utilization_percentage
Variable Management
list_variables(limit=20, offset=0, order_by="key")List all variables stored in Airflow with pagination support. Output:variables,total_entries,limit,offset, variable details with keys, values, and descriptionsget_variable(variable_key)Get detailed information about a specific variable by its key. Output:key,value,description,is_encrypted
Task Instance Management
list_task_instances_all(dag_id=None, dag_run_id=None, execution_date_gte=None, execution_date_lte=None, start_date_gte=None, start_date_lte=None, end_date_gte=None, end_date_lte=None, duration_gte=None, duration_lte=None, state=None, pool=None, queue=None, limit=20, offset=0)Lists task instances across all DAGs or filtered by specific criteria with comprehensive filtering options. Output:task_instances,total_entries,limit,offset,applied_filtersget_task_instance_details(dag_id, dag_run_id, task_id)Retrieves detailed information about a specific task instance. Output: Comprehensive task instance details including execution info, state, timing, configuration, and metadatalist_task_instances_batch(dag_ids=None, dag_run_ids=None, task_ids=None, execution_date_gte=None, execution_date_lte=None, start_date_gte=None, start_date_lte=None, end_date_gte=None, end_date_lte=None, duration_gte=None, duration_lte=None, state=None, pool=None, queue=None)Lists task instances in batch with multiple filtering criteria for bulk operations. Output:task_instances,total_entries,applied_filters, batch processing resultsget_task_instance_extra_links(dag_id, dag_run_id, task_id)Lists extra links for a specific task instance (e.g., monitoring dashboards, logs, external resources). Output:task_id,dag_id,dag_run_id,extra_links,total_linksget_task_instance_logs(dag_id, dag_run_id, task_id, try_number=1, full_content=False, token=None)Retrieves logs for a specific task instance and its try number with content and metadata. Output:task_id,dag_id,dag_run_id,try_number,content,continuation_token,metadata
XCom Management
list_xcom_entries(dag_id, dag_run_id, task_id, limit=20, offset=0)Lists XCom entries for a specific task instance. Output:dag_id,dag_run_id,task_id,xcom_entries,total_entries,limit,offsetget_xcom_entry(dag_id, dag_run_id, task_id, xcom_key, map_index=-1)Retrieves a specific XCom entry for a task instance. Output:dag_id,dag_run_id,task_id,xcom_key,map_index,key,value,timestamp,execution_date,run_id
DAG Analysis & Monitoring
get_dag(dag_id)Retrieves comprehensive details for a specific DAG. Output:dag_id,description,schedule_interval,owners,tags,start_date,next_dagrun, etc.dag_graph(dag_id)Retrieves task dependency graph structure for a specific DAG. Output:dag_id,tasks,dependencies, task relationshipslist_tasks(dag_id)Lists all tasks for a specific DAG. Output:dag_id,tasks, task configuration details Output:dag_id,tasks,dependencies, task relationshipsdag_code(dag_id)Retrieves the source code for a specific DAG. Output:dag_id,file_token,source_codelist_event_logs(dag_id=None, task_id=None, run_id=None, limit=20, offset=0)Lists event log entries with optional filtering. Optimized limit: Default is 20 for better performance while maintaining good coverage. Output:event_logs,total_entries,limit,offset,has_more_pages,next_offset,pagination_infoget_event_log(event_log_id)Retrieves a specific event log entry by ID. Output:event_log_id,when,event,dag_id,task_id,run_id, etc.all_dag_event_summary()Retrieves event count summary for all DAGs. Improved limit: Uses limit=1000 for DAG retrieval to avoid missing DAGs in large environments. Output:dag_summaries,total_dags,total_eventslist_import_errors(limit=20, offset=0)Lists import errors with optional filtering. Optimized limit: Default is 20 for better performance while maintaining good coverage. Output:import_errors,total_entries,limit,offset,has_more_pages,next_offset,pagination_infoget_import_error(import_error_id)Retrieves a specific import error by ID. Output:import_error_id,filename,stacktrace,timestampall_dag_import_summary()Retrieves import error summary for all DAGs. Output:import_summaries,total_errors,affected_filesdag_run_duration(dag_id, limit=50)Retrieves run duration statistics for a specific DAG. Improved limit: Default increased from 10 to 50 for better statistical analysis. Output:dag_id,runs, duration analysis, success/failure statsdag_task_duration(dag_id, run_id=None)Retrieves task duration information for a specific DAG run. Output:dag_id,run_id,tasks, individual task performancedag_calendar(dag_id, start_date=None, end_date=None, limit=20)Retrieves calendar/schedule information for a specific DAG. Configurable limit: Default is 20, can be increased up to 1000 for bulk analysis. Output:dag_id,schedule_interval,runs, upcoming executions
Example Queries
Go to Example Queries
Prompt Template
The package exposes a tool get_prompt_template that returns either the entire template, a specific section, or just the headings. Three MCP prompts (prompt_template_full, prompt_template_headings, prompt_template_section) are also registered for discovery.
MCP Prompts
For easier discoverability in MCP clients (so prompts/list is not empty), the server now registers three prompts:
• prompt_template_full – returns the full canonical template • prompt_template_headings – returns only the section headings • prompt_template_section – takes a section argument (number or keyword) and returns that section
You can still use the get_prompt_template tool for programmatic access or when you prefer tool invocation over prompt retrieval.
Single canonical English prompt template guides safe and efficient tool selection.
Files:• Packaged: src/mcp_airflow_api/prompt_template.md (distributed with PyPI) • (Optional workspace root copy PROMPT_TEMPLATE.md may exist for editing; packaged copy is the one loaded at runtime.)
Retrieve dynamically via MCP tool:• get_prompt_template() – full template • get_prompt_template("tool map") – only the tool mapping section • get_prompt_template("3") – section 3 (tool map) • get_prompt_template(mode="headings") – list all section headings
Policy: Only English is stored; the LLM always uses English instructions for internal reasoning, regardless of the user's query language. User responses may be generated in multiple languages as needed.
Main Tool Files
- MCP tool definitions:
src/mcp_airflow_api/airflow_api.py - Utility functions:
src/mcp_airflow_api/functions.py
Pagination Guide for Large Airflow Environments
Understanding DAG Pagination
The list_dags() function now supports pagination to handle large Airflow environments efficiently:
Default Behavior:
- Returns first 100 DAGs by default
- Includes pagination metadata in response
Pagination Response Structure:
{
"dags": [...],
"total_entries": 1500,
"limit": 100,
"offset": 0,
"returned_count": 100,
"has_more_pages": true,
"next_offset": 100,
"pagination_info": {
"current_page": 1,
"total_pages": 15,
"remaining_count": 1400
}
}
Pagination Strategies
🔍 Exploratory (Recommended for LLMs):
1. list_dags() → Check first 20 DAGs
2. Use has_more_pages to determine if more exist
3. list_dags(limit=20, offset=20) → Get next 20
4. Continue as needed
📊 Complete Analysis:
→ Automatically fetches ALL DAGs regardless of count
⚡ Quick Large Queries:
list_dags(limit=500)
→ Get up to 500 DAGs in one call
Best Practices
- Small Airflow (< 50 DAGs): Use default
list_dags() - Medium Airflow (50-500 DAGs): Use
list_dags(limit=100)orlist_dags(limit=200) - Memory-conscious: Use default limits (20) with manual pagination
Logging & Observability
- Structured logs for all tool invocations and HTTP requests
- Control log level via environment variable (
AIRFLOW_LOG_LEVEL) or CLI flag (--log-level) - Supported levels: DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL
Roadmap
This project starts with a minimal set of essential Airflow management tools. Many more useful features and tools for Airflow cluster operations will be added soon, including advanced monitoring, DAG/task analytics, scheduling controls, and more. Contributions and suggestions are welcome!
Additional Links
Testing
This project includes comprehensive tests for the prompt template functionality.
Running Tests
# Install development dependencies
uv sync
# Run all tests
uv run pytest
# Run tests with verbose output
uv run pytest -v
# Run specific test file
uv run pytest tests/test_prompt_template.py -v
More ScreenShoots

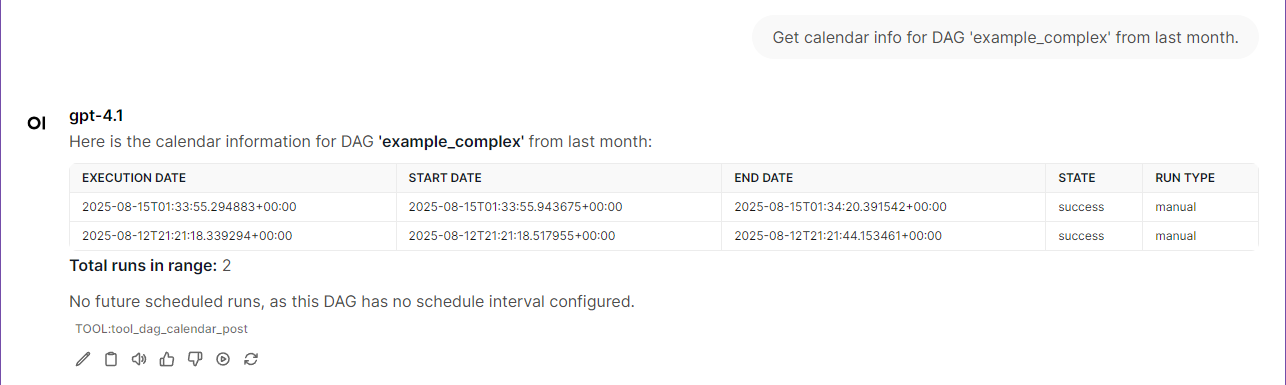
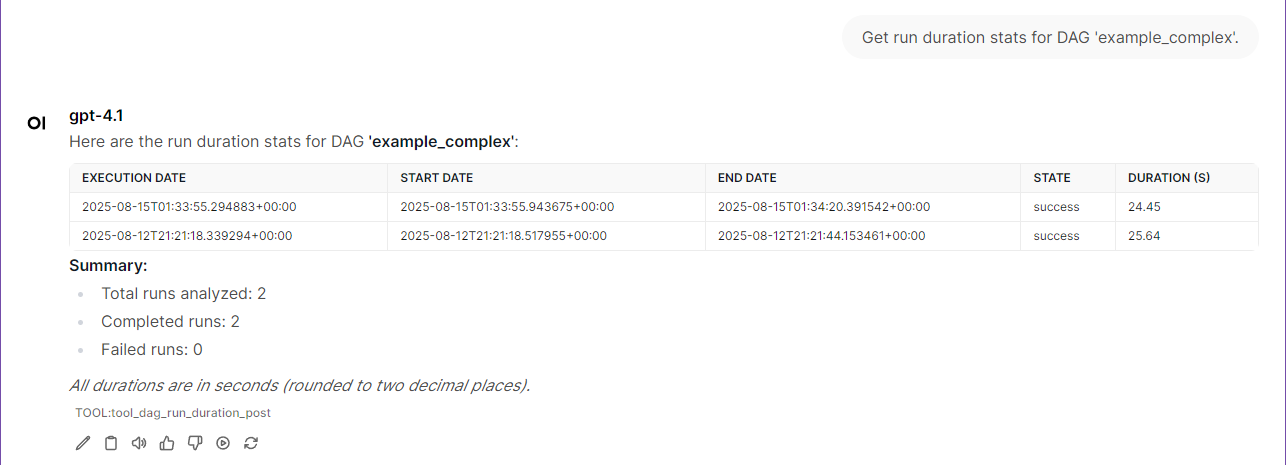
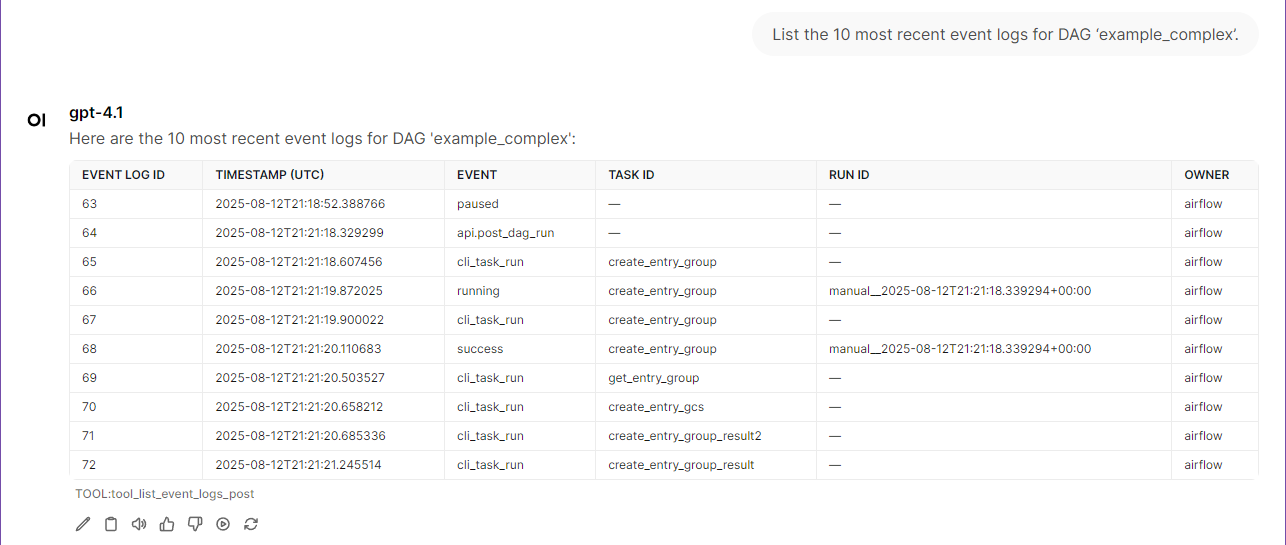
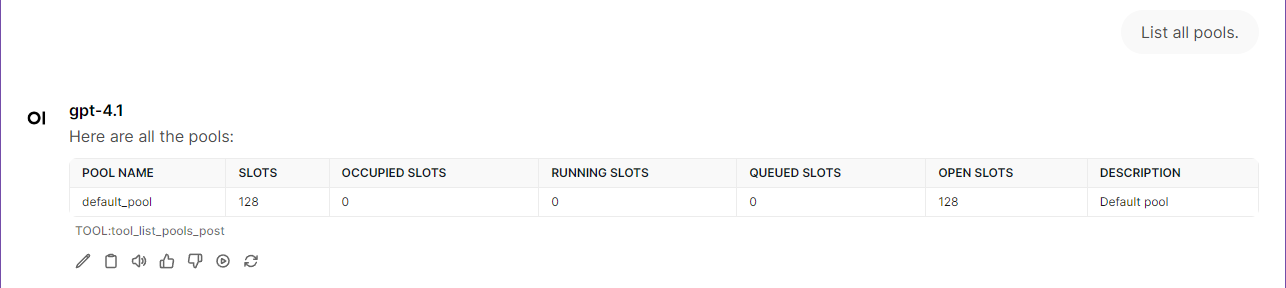
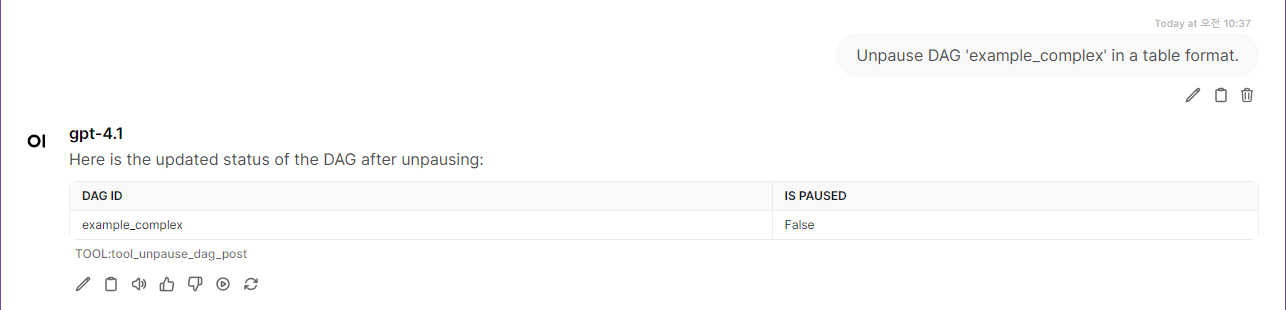
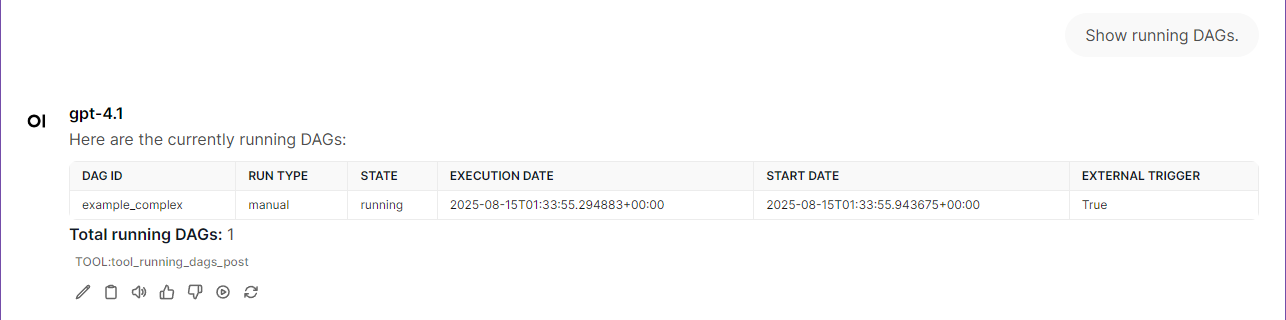
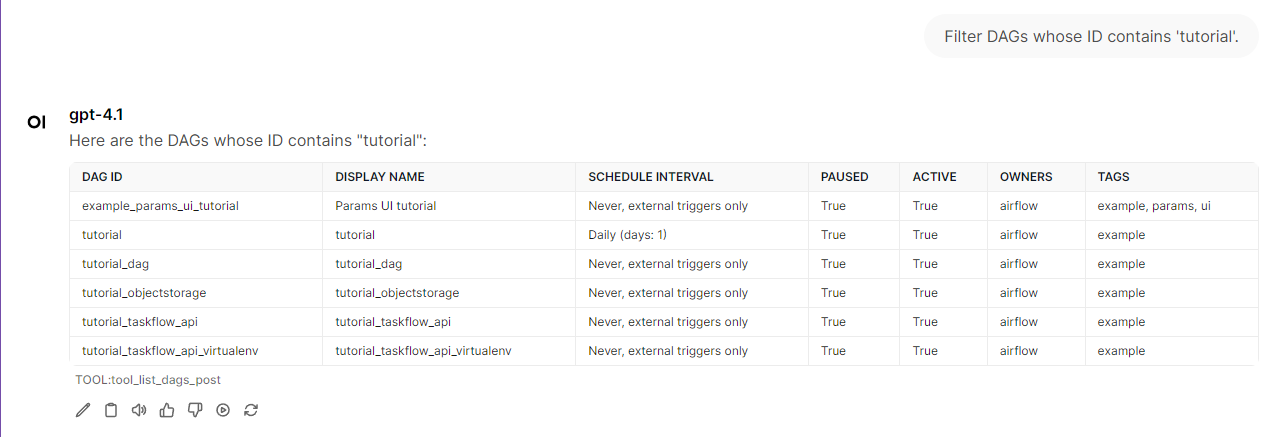

License
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
