MCP PostgreSQL Operations Server
A professional MCP server for PostgreSQL database server operations, monitoring, and management. Most features work independently, but advanced performance analysis capabilities are available when the pg_stat_statements and (optionally) pg_stat_monitor extensions are installed.
Features
✅ Version Compatibility: Automatic PostgreSQL version detection with adaptive functionality (12-18)
✅ PostgreSQL Monitoring: Performance analysis based on pg_stat_statements and pg_stat_monitor
✅ Structure Exploration: Database, table, and user listing
✅ Performance Analysis: Slow query identification and index usage analysis
✅ Capacity Management: Database and table size analysis
✅ Configuration Retrieval: PostgreSQL configuration parameter verification
✅ Database Performance Statistics: Comprehensive transaction, I/O, and buffer cache analysis
✅ I/O Performance Monitoring: Version-aware I/O statistics (comprehensive on PG16+, basic on PG12-15)
✅ Background Process Monitoring: Version-aware checkpoint and background writer analysis (split on PG15+)
✅ Replication Monitoring: Standby server conflict detection and replication lag analysis
✅ Function Performance Analysis: User-defined function execution statistics
✅ Safe Read-Only: All operations are read-only and safe
🛠️ Easy Customization: Simple and clean codebase makes it very easy to add new tools or customize existing ones
Example Usage
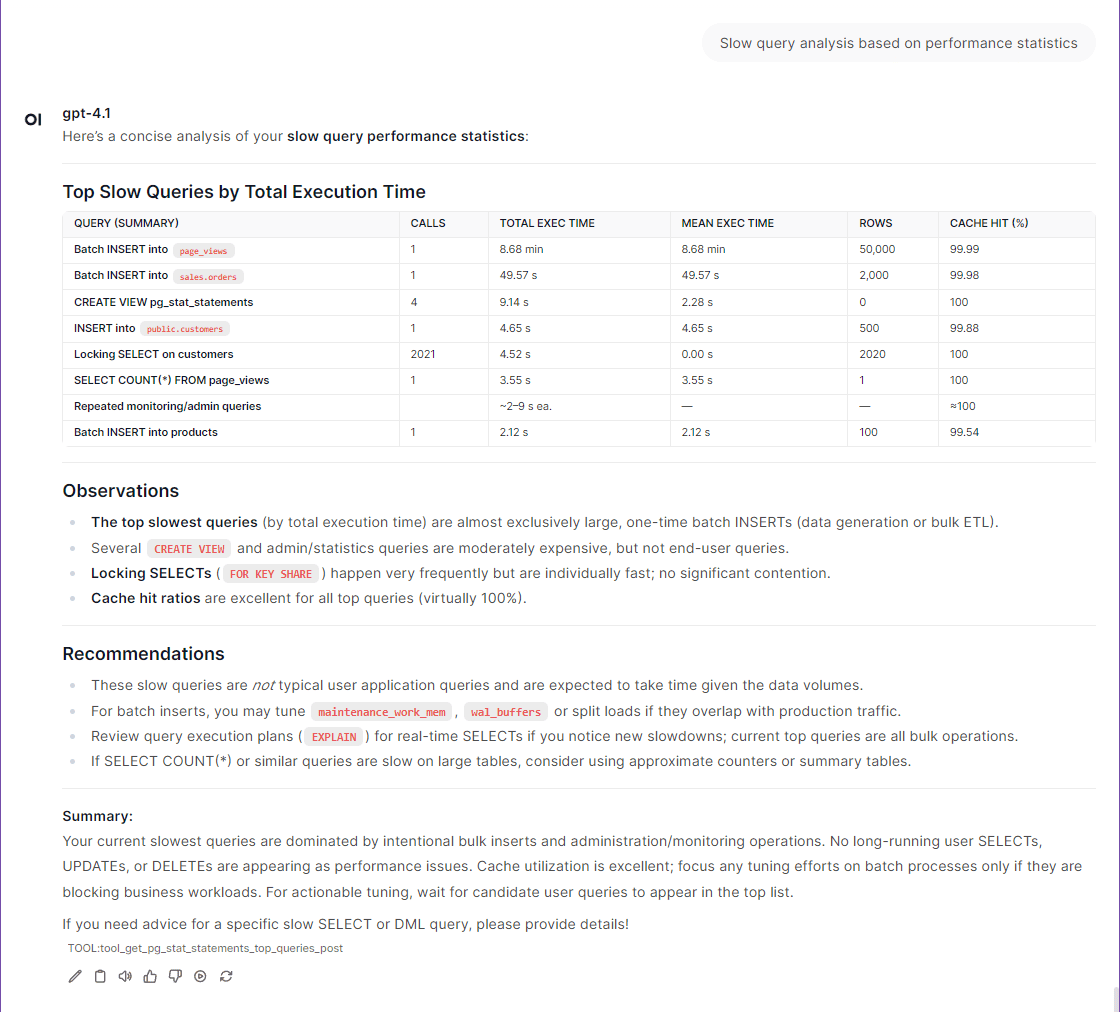
Quick start
Note: The
postgresqlcontainer included indocker-compose.ymlis intended for quickstart testing purposes only. You can connect to your own PostgreSQL instance by adjusting the environment variables as needed.
If you want to use your own PostgreSQL instance instead of the built-in test container:
- Update the target PostgreSQL connection information in your
.envfile (see POSTGRES_HOST, POSTGRES_PORT, POSTGRES_USER, POSTGRES_PASSWORD, POSTGRES_DB).- In
docker-compose.yml, comment out (disable) thepostgresandpostgres-init-extensionscontainers to avoid starting the built-in test database.
1. Environment Setup
Note: While superuser privileges provide access to all databases and system information, the MCP server also works with regular user permissions for basic monitoring tasks.
### Check and modify .env file
cp .env.example .env
### If you use other postgresql server, configure connection information:
POSTGRES_HOST=your-address
POSTGRES_PORT=your-listen-port
POSTGRES_USER=your-username
POSTGRES_PASSWORD=your-password
POSTGRES_DB=your-database # Default connection DB. Superusers can access all DBs.
2. Install Dependencies
docker-compose up -d
3. Access to OpenWebUI
- The list of MCP tool features provided by
swaggercan be found in the MCPO API Docs URL.- e.g:
http://localhost:8003/docs
- e.g:
4. Registering the Tool in OpenWebUI
- logging in to OpenWebUI with an admin account
- go to "Settings" → "Tools" from the top menu.
- Enter the
postgresql-opsTool address (e.g.,http://localhost:8003/postgresql-ops) to connect MCP Tools. - Setup Ollama or OpenAI.
Version Compatibility
✅ Supported Versions: PostgreSQL 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18
This MCP server automatically detects your PostgreSQL version and adapts its functionality accordingly:
- PostgreSQL 16+: Full feature support including comprehensive I/O statistics (
pg_stat_io) - PostgreSQL 15+: Enhanced background process monitoring with separate checkpointer stats
- PostgreSQL 14+: Parallel query tracking and replication slot statistics
- PostgreSQL 13+: Query ID support for performance correlation
- PostgreSQL 12+: Core functionality with all essential monitoring tools
🔄 Automatic Adaptation: All tools work transparently across supported versions - no configuration needed!
Usage Examples
Claude Desktop Integration
(Recommended) Add to your Claude Desktop configuration file:
{
"mcpServers": {
"postgresql-ops": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["--python", "3.11", "mcp-postgresql-ops"],
"env": {
"POSTGRES_HOST": "127.0.0.1",
"POSTGRES_PORT": "5432",
"POSTGRES_USER": "postgres",
"POSTGRES_PASSWORD": "passwd",
"POSTGRES_DB": "testdb"
}
}
}
}

(Optional) Run with Local Source:
{
"mcpServers": {
"postgresql-ops": {
"command": "uv",
"args": ["run", "python", "-m", "src.mcp_postgresql_ops.mcp_main"],
"cwd": "/path/to/MCP-PostgreSQL-Ops",
"env": {
"POSTGRES_HOST": "127.0.0.1",
"POSTGRES_PORT": "5432",
"POSTGRES_USER": "postgres",
"POSTGRES_PASSWORD": "passwd",
"POSTGRES_DB": "testdb"
}
}
}
}
Command Line Usage
/w Pypi and uvx (Recommended)
# Stdio mode
uvx --python 3.11 mcp-postgresql-ops \
--type stdio
# HTTP mode
uvx --python 3.11 mcp-postgresql-ops
--type streamable-http \
--host 127.0.0.1 \
--port 8080 \
--log-level DEBUG
/w Local Source
# Stdio mode
PYTHONPATH=/path/to/MCP-PostgreSQL-Ops
python -m src.mcp_postgresql_ops.mcp_main \
--type stdio
# HTTP mode
PYTHONPATH=/path/to/MCP-PostgreSQL-Ops
python -m src.mcp_postgresql_ops.mcp_main \
--type streamable-http \
--host 127.0.0.1 \
--port 8080 \
--log-level DEBUG
Environment Variables
| Variable | Description | Default | Project Default |
|---|---|---|---|
PYTHONPATH |
Python module search path for MCP server imports | - | /app/src |
MCP_LOG_LEVEL |
Server logging verbosity (DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR) | INFO |
INFO |
FASTMCP_TYPE |
MCP transport protocol (stdio for CLI, streamable-http for web) | stdio |
streamable-http |
FASTMCP_HOST |
HTTP server bind address (0.0.0.0 for all interfaces) | 127.0.0.1 |
0.0.0.0 |
FASTMCP_PORT |
HTTP server port for MCP communication | 8080 |
8080 |
PGSQL_VERSION |
PostgreSQL major version for Docker image selection | 16 |
16 |
POSTGRES_HOST |
PostgreSQL server hostname or IP address | 127.0.0.1 |
host.docker.internal |
POSTGRES_PORT |
PostgreSQL server port number | 5432 |
15432 |
POSTGRES_USER |
PostgreSQL connection username (needs read permissions) | postgres |
postgres |
POSTGRES_PASSWORD |
PostgreSQL user password (supports special characters) | changeme!@34 |
changeme!@34 |
POSTGRES_DB |
Default database name for connections | testdb |
testdb |
POSTGRES_MAX_CONNECTIONS |
PostgreSQL max_connections configuration parameter | 200 |
200 |
DOCKER_EXTERNAL_PORT_OPENWEBUI |
Host port mapping for Open WebUI container | 8080 |
3003 |
DOCKER_EXTERNAL_PORT_MCP_SERVER |
Host port mapping for MCP server container | 8080 |
18003 |
DOCKER_EXTERNAL_PORT_MCPO_PROXY |
Host port mapping for MCPO proxy container | 8000 |
8003 |
Note: POSTGRES_DB serves as the default target database for operations when no specific database is specified. In Docker environments, if set to a non-default name, this database will be automatically created during initial PostgreSQL startup.
Prerequisites
Required PostgreSQL Extensions
⚠️ Note:Most MCP tools work without any PostgreSQL extensions.However, advanced performance analysis tools require the following extensions:
-- Query performance statistics (required only for get_pg_stat_statements_top_queries)
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pg_stat_statements;
-- Advanced monitoring (optional, used by get_pg_stat_monitor_recent_queries)
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pg_stat_monitor;
Quick Setup: For new PostgreSQL installations, add to postgresql.conf:
shared_preload_libraries = 'pg_stat_statements'
Then restart PostgreSQL and run the CREATE EXTENSION commands above.
pg_stat_statementsis required only for slow query analysis tools.pg_stat_monitoris optional and used for real-time query monitoring.- All other tools work without these extensions.
Minimum Requirements
- PostgreSQL 12+ (tested with PostgreSQL 16)
- Python 3.11
- Network access to PostgreSQL server
- Read permissions on system catalogs
Required PostgreSQL Configuration
⚠️ Statistics Collection Settings:Some MCP tools require specific PostgreSQL configuration parameters to collect statistics. Choose one of the following configuration methods:
Tools affected by these settings:
- get_user_functions_stats: Requires
track_functions = plortrack_functions = all - get_table_io_stats & get_index_io_stats: More accurate timing with
track_io_timing = on - get_database_stats: Enhanced I/O timing with
track_io_timing = on
Verification:After applying any method, verify the settings:
SELECT name, setting, context FROM pg_settings WHERE name IN ('track_activities', 'track_counts', 'track_io_timing', 'track_functions') ORDER BY name;
name | setting | context
------------------+---------+-----------
track_activities | on | superuser
track_counts | on | superuser
track_functions | pl | superuser
track_io_timing | on | superuser
(4 rows)
Method 1: postgresql.conf (Recommended for Self-Managed PostgreSQL)
Add the following to your postgresql.conf:
# Basic statistics collection (usually enabled by default)
track_activities = on
track_counts = on
# Required for function statistics tools
track_functions = pl # Enables PL/pgSQL function statistics collection
# Optional but recommended for accurate I/O timing
track_io_timing = on # Enables I/O timing statistics collection
Then restart PostgreSQL server.
Method 2: PostgreSQL Startup Parameters
For Docker or command-line PostgreSQL startup:
# Docker example
docker run -d \
-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mypassword \
postgres:16 \
-c track_activities=on \
-c track_counts=on \
-c track_functions=pl \
-c track_io_timing=on
# Direct postgres command
postgres -D /data \
-c track_activities=on \
-c track_counts=on \
-c track_functions=pl \
-c track_io_timing=on
Method 3: Dynamic Configuration (AWS RDS, Azure, GCP, Managed Services)
For managed PostgreSQL services where you cannot modify postgresql.conf, use SQL commands to change settings dynamically:
-- Enable basic statistics collection (usually enabled by default)
ALTER SYSTEM SET track_activities = 'on';
ALTER SYSTEM SET track_counts = 'on';
-- Enable function statistics collection (requires superuser privileges)
ALTER SYSTEM SET track_functions = 'pl';
-- Enable I/O timing statistics (optional but recommended)
ALTER SYSTEM SET track_io_timing = 'on';
-- Reload configuration without restart (run separately)
SELECT pg_reload_conf();
Alternative for session-level testing:
-- Set for current session only (temporary)
SET track_activities = 'on';
SET track_counts = 'on';
SET track_functions = 'pl';
SET track_io_timing = 'on';
Note: When using command-line tools, run each SQL statement separately to avoid transaction block errors.
Example Queries
🟢 Extension-Independent Tools (Always Available)
- get_server_info
- "Show PostgreSQL server version and extension status"
- "Check if pg_stat_statements is installed"
- get_active_connections
- "Show all active connections"
- "List current sessions with database and user"
- get_postgresql_config
- "Show all PostgreSQL configuration parameters"
- "Find all memory-related configuration settings"
- get_database_list
- "List all databases and their sizes"
- "Show database list with owner information"
- get_table_list
- "List all tables in the current database"
- "Show table sizes in the public schema"
- get_user_list
- "List all database users and their roles"
- "Show user permissions for a specific database"
- get_index_usage_stats
- "Analyze index usage efficiency"
- "Find unused indexes in the current database"
- get_database_size_info
- "Show database capacity analysis"
- "Find the largest databases by size"
- get_table_size_info
- "Show table and index size analysis"
- "Find largest tables in a specific schema"
- get_vacuum_analyze_stats
- "Show recent VACUUM and ANALYZE operations"
- "List tables needing VACUUM"
- get_lock_monitoring
- "Show all current locks and blocked sessions"
- "Show only blocked sessions with granted=false filter"
- "Monitor locks by specific user with username filter"
- "Check exclusive locks with mode filter"
- get_wal_status
- "Show WAL status and archiving information"
- "Monitor WAL generation and current LSN position"
- get_replication_status
- "Check replication connections and lag status"
- "Monitor replication slots and WAL receiver status"
- get_database_stats
- "Show comprehensive database performance metrics"
- "Analyze transaction commit ratios and I/O statistics"
- "Monitor buffer cache hit ratios and temporary file usage"
- get_bgwriter_stats
- "Analyze checkpoint performance and timing"
- "Show background writer efficiency statistics"
- "Monitor buffer allocation and fsync patterns"
- get_all_tables_stats
- "Show comprehensive statistics for all tables"
- "Include system tables with include_system=true parameter"
- "Analyze table access patterns and maintenance needs"
- get_user_functions_stats
- "Analyze user-defined function performance"
- "Show function call counts and execution times"
- "Identify performance bottlenecks in custom functions"
- ⚠️ Requires:
track_functions = plin postgresql.conf
- get_table_io_stats
- "Analyze table I/O performance and buffer hit ratios"
- "Identify tables with poor buffer cache performance"
- "Monitor TOAST table I/O statistics"
- 💡 Enhanced with:
track_io_timing = onfor accurate timing
- get_index_io_stats
- "Show index I/O performance and buffer efficiency"
- "Identify indexes causing excessive disk I/O"
- "Monitor index cache-friendliness patterns"
- 💡 Enhanced with:
track_io_timing = onfor accurate timing
- get_database_conflicts_stats
- "Check replication conflicts on standby servers"
- "Analyze conflict types and resolution statistics"
- "Monitor standby server query cancellation patterns"
- "Monitor WAL generation and current LSN position"
- get_replication_status
- "Check replication connections and lag status"
- "Monitor replication slots and WAL receiver status"
🚀 Version-Aware Tools (Auto-Adapting)
- get_io_stats (New!)
- "Show comprehensive I/O statistics" (PostgreSQL 16+ provides detailed breakdown)
- "Analyze buffer cache efficiency and I/O timing"
- "Monitor I/O patterns by backend type and context"
- 📈 PG16+: Full pg_stat_io with timing, backend types, and contexts
- 📊 PG12-15: Basic pg_statio_* fallback with buffer hit ratios
- get_bgwriter_stats (Enhanced!)
- "Show background writer and checkpoint performance"
- 📈 PG15+: Separate checkpointer and bgwriter statistics
- 📊 PG12-14: Combined bgwriter stats (includes checkpointer data)
- get_server_info (Enhanced!)
- "Show server version and compatibility features"
- "Check what MCP tools are available on this PostgreSQL version"
- Displays feature availability matrix and upgrade recommendations
🟡 Extension-Dependent Tools
- get_pg_stat_statements_top_queries (Requires
pg_stat_statements)- "Show top 10 slowest queries"
- "Analyze slow queries in the sales database"
- get_pg_stat_monitor_recent_queries (Optional, uses
pg_stat_monitor)- "Show recent queries in real time"
- "Monitor query activity for the last 5 minutes"
💡 Pro Tip: All tools support multi-database operations using the database_name parameter. This allows PostgreSQL superusers to analyze and monitor multiple databases from a single MCP server instance.
📖 More Useful Example Queries →
Troubleshooting
Connection Issues
- Check PostgreSQL server status
- Verify connection parameters in
.envfile - Ensure network connectivity
- Check user permissions
Extension Errors
- Run
get_server_infoto check extension status - Install missing extensions:
CREATE EXTENSION pg_stat_statements; CREATE EXTENSION pg_stat_monitor; - Restart PostgreSQL if needed
Configuration Issues
"No data found" for function statistics: Check
track_functionssettingSHOW track_functions; -- Should be 'pl' or 'all'Quick fix for managed services (AWS RDS, etc.):
ALTER SYSTEM SET track_functions = 'pl'; SELECT pg_reload_conf();Missing I/O timing data: Enable timing collection
SHOW track_io_timing; -- Should be 'on'Quick fix:
ALTER SYSTEM SET track_io_timing = 'on'; SELECT pg_reload_conf();Apply configuration changes:
- Self-managed: Add settings to
postgresql.confand restart server - Managed services: Use
ALTER SYSTEM SET+SELECT pg_reload_conf() - Temporary testing: Use
SET parameter = valuefor current session - Generate some database activity to populate statistics
- Self-managed: Add settings to
Performance Issues
- Use
limitparameters to reduce result size - Run monitoring during off-peak hours
- Check database load before running analysis
Version Compatibility Issues
Run compatibility check first:
# Use get_server_info to check version and available featuresUnderstanding feature availability:
- PostgreSQL 16+: All features available
- PostgreSQL 15+: Separate checkpointer stats
- PostgreSQL 14+: Parallel query tracking
- PostgreSQL 12-13: Core functionality only
If a tool shows "Not Available":
- Feature requires newer PostgreSQL version
- Tool will automatically use best available alternative
- Consider upgrading PostgreSQL for enhanced monitoring
Development
Testing & Development
# Test with MCP Inspector
./scripts/run-mcp-inspector-local.sh
# Direct execution for debugging
python -m src.mcp_postgresql_ops.mcp_main --log-level DEBUG
# Test version compatibility (requires different PostgreSQL versions)
# Modify POSTGRES_HOST in .env to point to different versions
# Run tests (if you add any)
uv run pytest
Version Compatibility Testing
The MCP server automatically adapts to PostgreSQL versions 12-18. To test across versions:
- Set up test databases: Different PostgreSQL versions (12, 14, 15, 16+)
- Run compatibility tests: Point to each version and verify tool behavior
- Check feature detection: Ensure proper version detection and feature availability
- Verify fallback behavior: Confirm graceful degradation on older versions
Security Notes
- All tools are read-only - no data modification capabilities
- Sensitive information (passwords) are masked in outputs
- No direct SQL execution - only predefined queries
- Follows principle of least privilege
Contributing
🤝 Got ideas? Found bugs? Want to add cool features?
We're always excited to welcome new contributors! Whether you're fixing a typo, adding a new monitoring tool, or improving documentation - every contribution makes this project better.
Ways to contribute:
- 🐛 Report issues or bugs
- 💡 Suggest new PostgreSQL monitoring features
- 📝 Improve documentation
- 🚀 Submit pull requests
- ⭐ Star the repo if you find it useful!
Pro tip: The codebase is designed to be super friendly for adding new tools. Check out the existing @mcp.tool() functions in mcp_main.py.
Related Projects
Other MCP servers by the same author:
License
Freely use, modify, and distribute under the MIT License.