What is Hindsight?
Hindsight™ is an agent memory system built to create smarter agents that learn over time. It eliminates the shortcomings of alternative techniques such as RAG and knowledge graph.
Hindsight addresses common challenges that have frustrated AI engineers building agents to automate tasks and assist users with conversational interfaces. Many of these challenges stem directly from a lack of memory.
- Inconsistency: Agents complete tasks successfully one time, then fail when asked to complete the same task again. Memory gives the agent a mechanism to remember what worked and what didn't and to use that information to reduce errors and improve consistency.
- Hallucinations: Long term memory can be seeded with external knowledge to ground agent behavior in reliable sources to augment training data.
- Cognitive Overload: As workflows get complex, retrievals, tool calls, user messages and agent responses can grow to fill the context window leading to context rot. Short term memory optimization allows agents to reduce tokens and focus context by removing irrelevant details.
How Hindsight Works
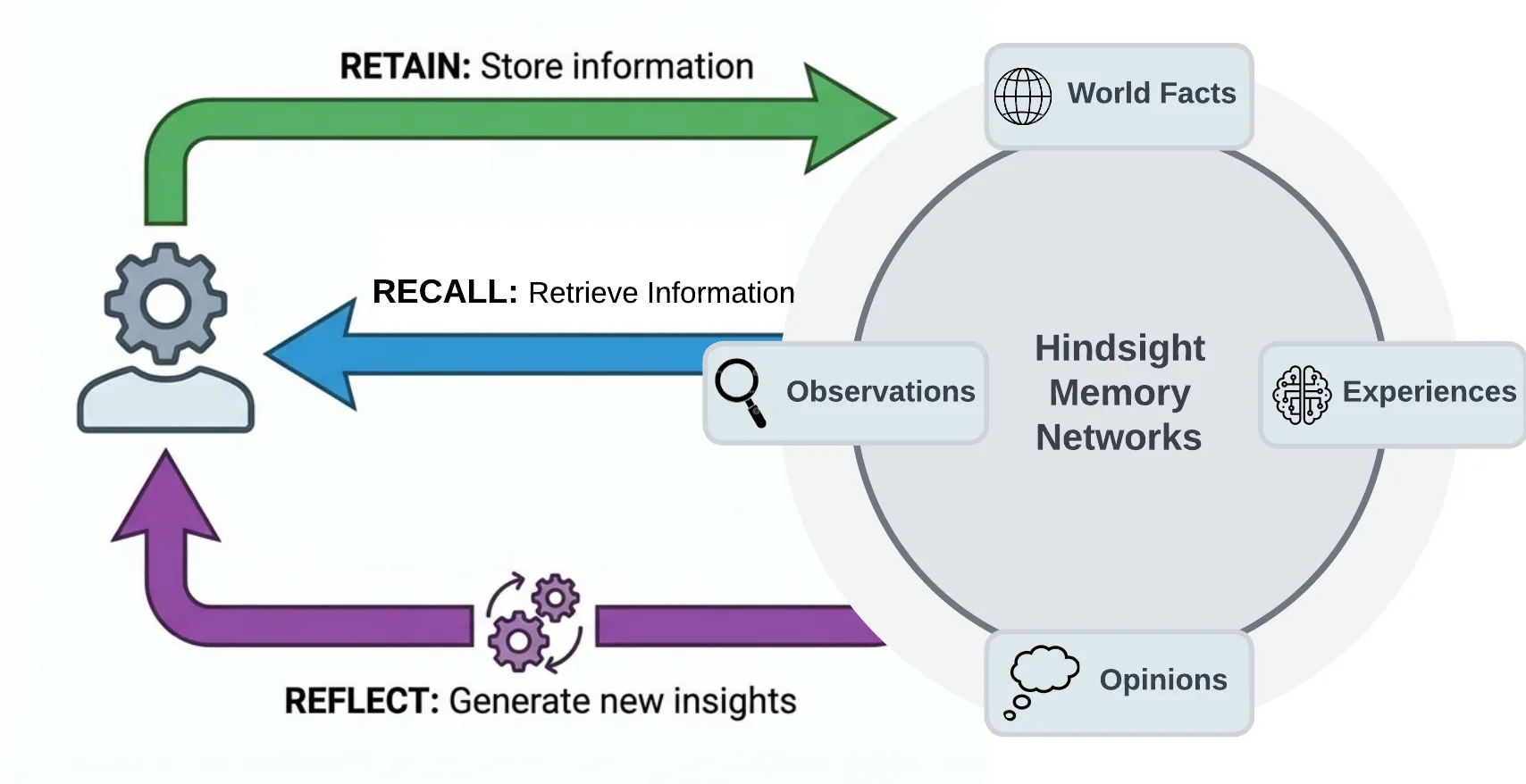
Hindsight organizes memory into four networks to mimic the way human memory works:
- World: Facts about the world ("The stove gets hot")
- Experiences: Agent's own experiences ("I touched the stove and it really hurt")
- Opinion: Beliefs with confidence scores ("I shouldn't touch the stove again" - .99 confidence)
- Observation: Complex mental models derived by reflecting on facts and experiences ("Curling irons, ovens, and fire are also hot. I shouldn't touch those either.")
Hindsight provides three simple methods to interact with the system:
- Retain: Provide information to Hindsight that you want it to remember
- Recall: Retrieve memories from Hindsight
- Reflect: Reflect on memories and experiences to generate new observations and insights from existing memories.
Memories in Hindsight are stored in banks (e.g. memory banks). When memories are retained, they are transformed to construct a series of search indexes, time series data, and entity/relationship graphs.
Quick Start
Docker (recommended)
export OPENAI_API_KEY=your-key
docker run --rm -it --pull always -p 8888:8888 -p 9999:9999 \
-e HINDSIGHT_API_LLM_API_KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY \
-e HINDSIGHT_API_LLM_MODEL=o3-mini \
-v $HOME/.hindsight-docker:/home/hindsight/.pg0 \
ghcr.io/vectorize-io/hindsight:latest
API: http://localhost:8888 UI: http://localhost:9999
Install client:
pip install hindsight-client -U
# or
npm install @vectorize-io/hindsight-client
Python example:
from hindsight_client import Hindsight
client = Hindsight(base_url="http://localhost:8888")
# Retain: Store information
client.retain(bank_id="my-bank", content="Alice works at Google as a software engineer")
# Recall: Search memories
client.recall(bank_id="my-bank", query="What does Alice do?")
# Reflect: Generate disposition-aware response
client.reflect(bank_id="my-bank", query="Tell me about Alice")
Python (embedded, no Docker)
pip install hindsight-all -U
import os
from hindsight import HindsightServer, HindsightClient
with HindsightServer(
llm_provider="openai",
llm_model="gpt-5-mini",
llm_api_key=os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]
) as server:
client = HindsightClient(base_url=server.url)
client.retain(bank_id="my-bank", content="Alice works at Google")
results = client.recall(bank_id="my-bank", query="Where does Alice work?")
Node.js / TypeScript
npm install @vectorize-io/hindsight-client
const { HindsightClient } = require('@vectorize-io/hindsight-client');
const client = new HindsightClient({ baseUrl: 'http://localhost:8888' });
await client.retain('my-bank', 'Alice loves hiking in Yosemite');
await client.recall('my-bank', 'What does Alice like?');
Architecture & Operations
Retain
The retain operation is used to push new memories into Hindsight. It tells Hindsight to retain the information you pass in as an input.
from hindsight_client import Hindsight
client = Hindsight(base_url="http://localhost:8888")
# Simple
client.retain(
bank_id="my-bank",
content="Alice works at Google as a software engineer"
)
# With context and timestamp
client.retain(
bank_id="my-bank",
content="Alice got promoted to senior engineer",
context="career update",
timestamp="2025-06-15T10:00:00Z"
)
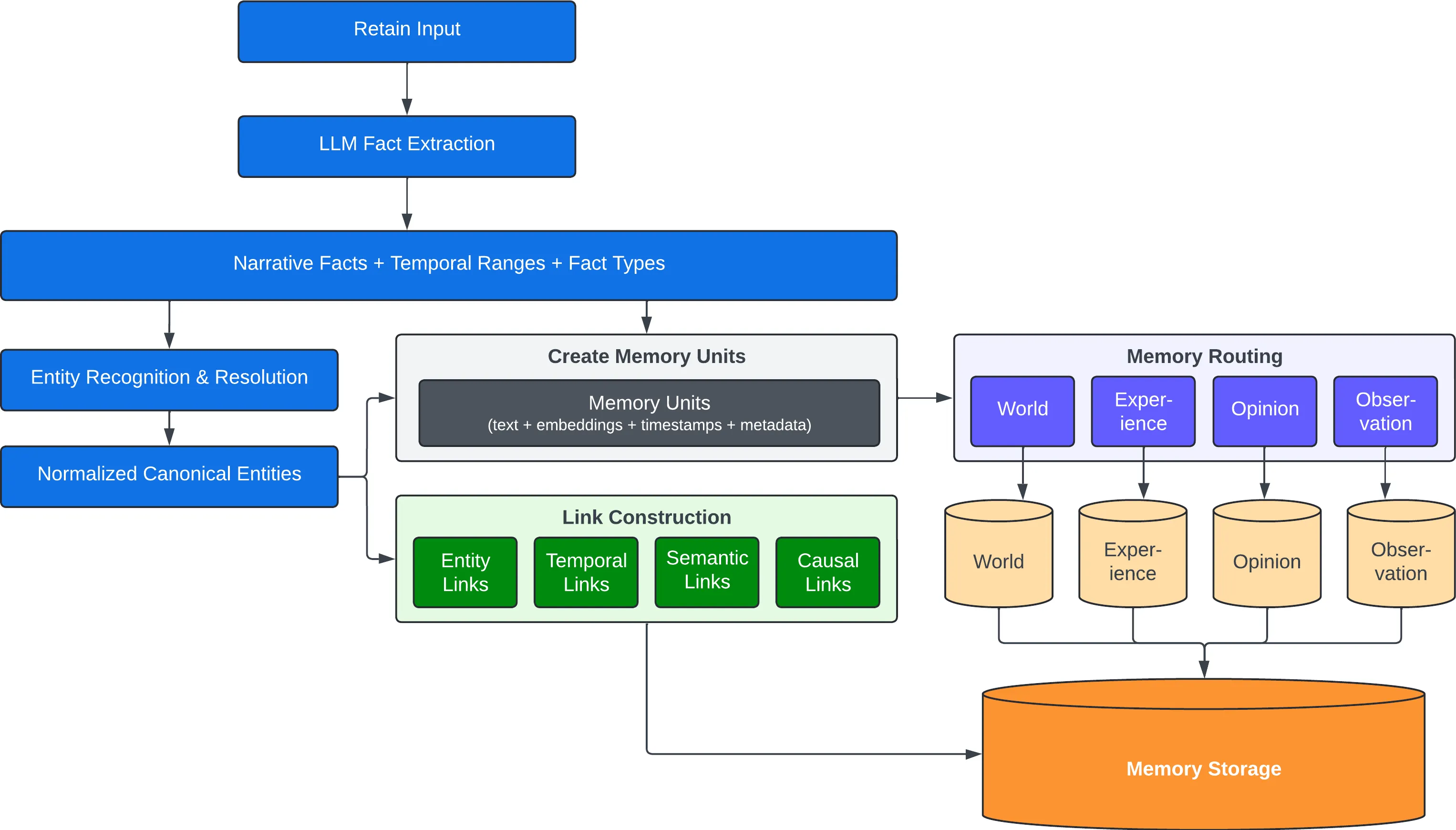
Behind the scenes, the retain operation uses an LLM to extract key facts, temporal data, entities, and relationships. It passes these through a normalization process to transform extracted data into canonical entities, time series, and search indexes along with metadata. These representations create the pathways for accurate memory retrieval in the recall and reflect operations.
Recall
The recall operation is used to retrieve memories. These memories can come from any of the memory types (world, experiences, etc.)
from hindsight_client import Hindsight
client = Hindsight(base_url="http://localhost:8888")
# Simple
client.recall(bank_id="my-bank", query="What does Alice do?")
# Temporal
client.recall(bank_id="my-bank", query="What happened in June?")
Recall performs 4 retrieval strategies in parallel:
- Semantic: Vector similarity
- Keyword: BM25 exact matching
- Graph: Entity/temporal/causal links
- Temporal: Time range filtering
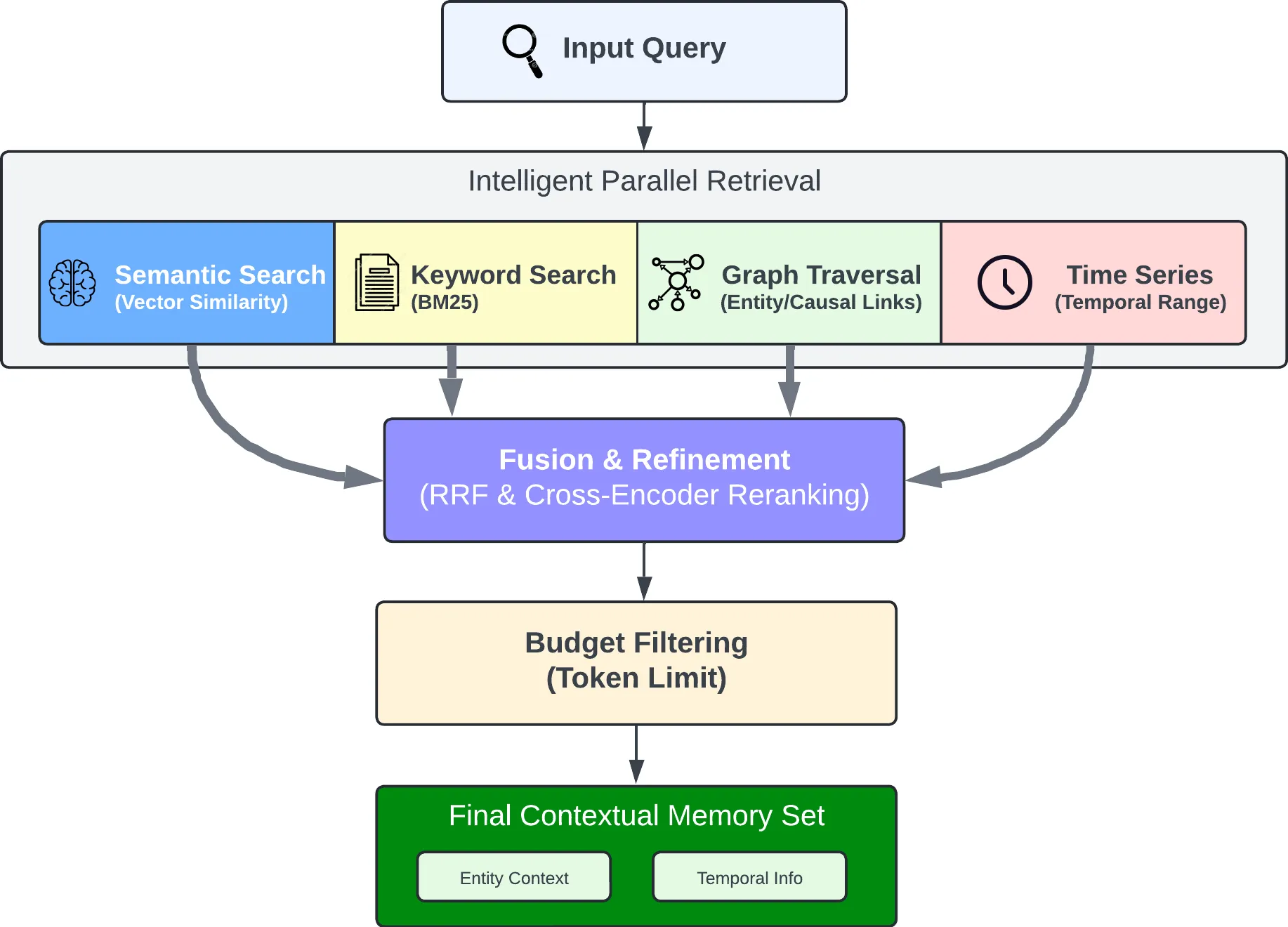
The individual results from the retrievals are merged, then ordered by relevance using reciprocal rank fusion and a cross-encoder reranking model.
The final output is trimmed as needed to fit within the token limit.
Reflect
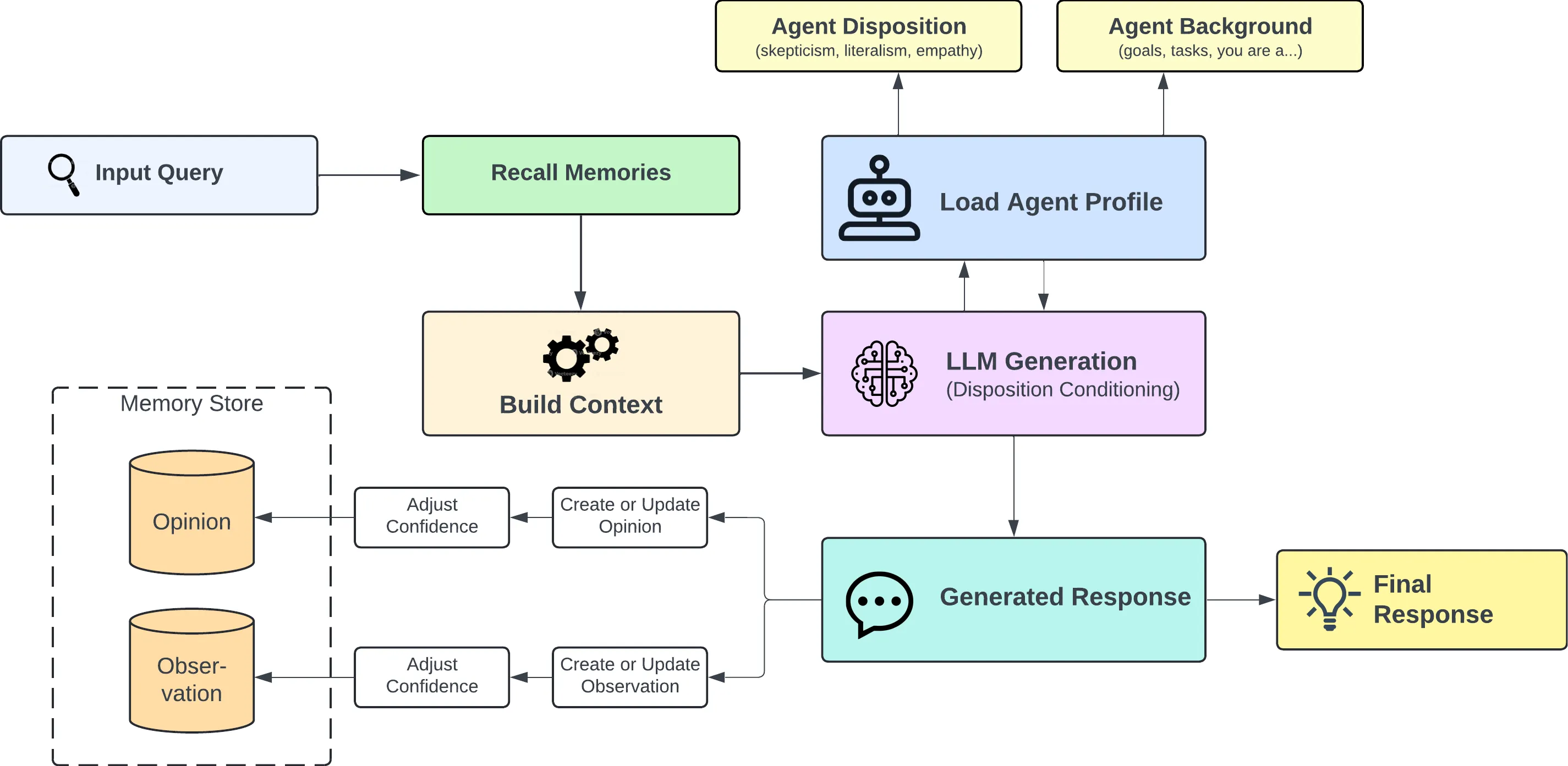
The reflect operation is used to perform a more thorough analysis of existing memories. This allows the agent to form new connections between memories which are then persisted as opinions and/or observations. When building agents, the reflect operation is a key capability to enable the agent to learn from its experiences.
For example, the reflect operation can be used to support use cases such as:
- An AI Project Manager reflecting on what risks need to be mitigated on a project.
- A Sales Agent reflecting on why certain outreach messages have gotten responses while others haven't.
- A Support Agent reflecting on opportunities where customers have questions not answered by current product documentation.
The reflect operation can also be used to handle on-demand question answering or analysis which require more deep thinking.
from hindsight_client import Hindsight
client = Hindsight(base_url="http://localhost:8888")
client.reflect(bank_id="my-bank", query="What should I know about Alice?")
Resources
Documentation:
Clients:
Community:
Contributing
See CONTRIBUTING.md.
License
MIT — see LICENSE
Built by Vectorize.io





